Yemen traditions, tourism, and their culture
Many years ago, a queen traveled from a faraway place called Saba to meet King Solomon in Jerusalem. She wanted to test his wisdom with riddles. The Bible says King Solomon answered all her questions wisely. Impressed, the Queen of Sheba gave him valuable gifts of gold and spices, making her land rich. She’s famous in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Artists from different places have drawn her in many ways. But did she really exist? No one’s sure. She became a legend, keeping the name of Saba alive.
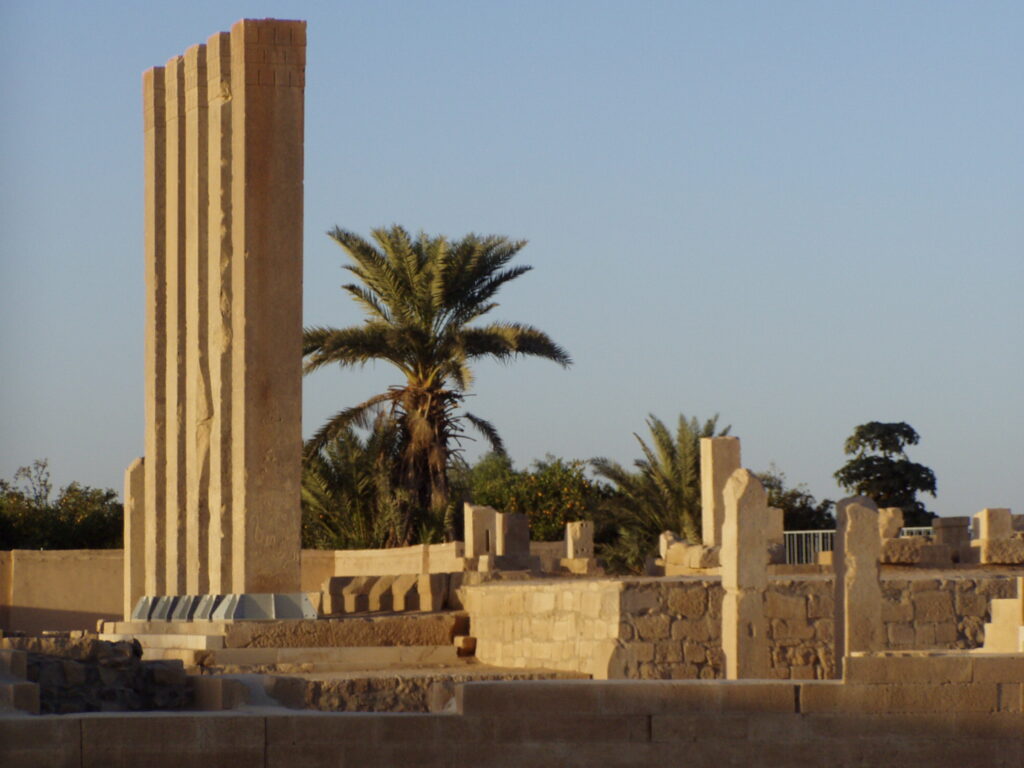

Some people in Yemen believe she lived there. Dr. Youssef Abdullah, Yemen’s director of antiquities, says there’s evidence in Yemen linking to her. There are ruins of the kingdom of Saba in Ma’rib. And the legend of the Queen of Sheba has been alive in Yemen for thousands of years. So, if she existed, Yemen is likely where she was from.

Yemen’s geography played a big role in its history. Three thousand years ago, Yemen was a hub for trade. Valuable items like frankincense were carried by camel caravans to faraway places. Yemen, at the bottom of the Arabian Peninsula, had periods of great wealth, especially in ancient times.
Tribes settled in towns near the desert, making money from trade. They became powerful kingdoms like Saba, Kataban, and Hadramaut. These kingdoms controlled the spice route for nearly a thousand years. Hadramaut, with its capital Shaba, was famous for producing frankincense. Explorers started uncovering Yemen’s history in the late 1800s. Despite challenges, they found beautiful landscapes, unique buildings, and friendly people.

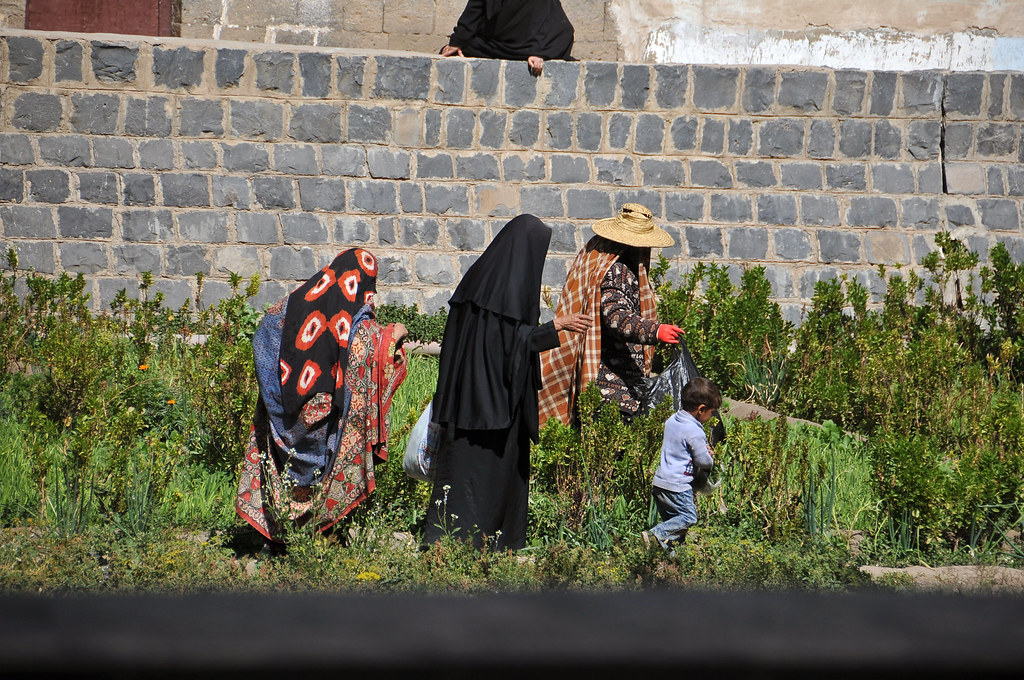
Yemen’s culture and religion are rich. Weddings, for example, last four days and involve the whole village. They include singing, shooting, and prayers. Yemen’s landscape is vast and dry, with deep valleys.
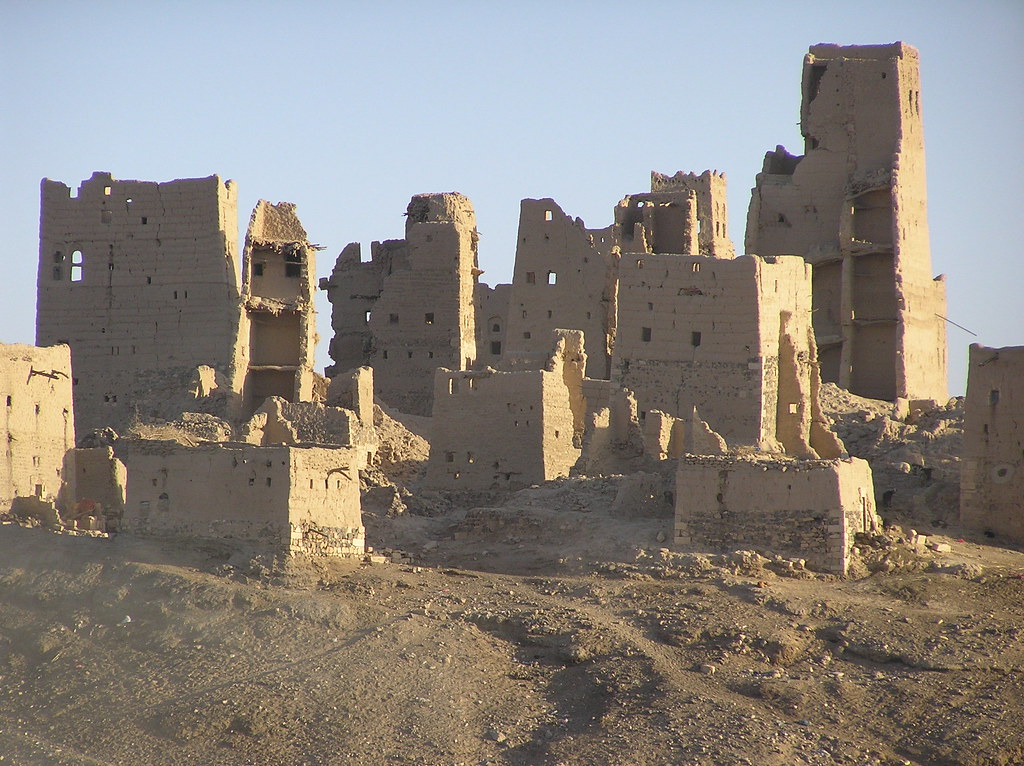
Long ago, frankincense trees were abundant here. Their resin was prized by many. The harvesting of frankincense led to stories and legends. Herodotus, a historian, wrote about colorful winged serpents protecting the trees. Today, frankincense trees are rare in Hadramaut. A few still grow on high plateaus. Harvesters collect resin from these trees using simple tools. In ancient times, Shaba, the capital of Hadramaut, was a bustling oasis. Drought turned it into a desert, where Bedouin families now live.

Salt was another important resource in ancient Yemen. Merchants brought salt, frankincense, and other goods to the capital. Shaba was a significant archaeological site. Pliny the Elder described it as a city with sixty temples. Recent discoveries confirm its importance in history.

In the olden days, Shaba was a very important place where people worshipped many gods. One of the most important gods was Almaqah, who was like a big strong bull. People would bring him gifts and sometimes even animals as presents. The temples in Shaba were not just for praying but also for doing important things like managing the city and trading stuff.
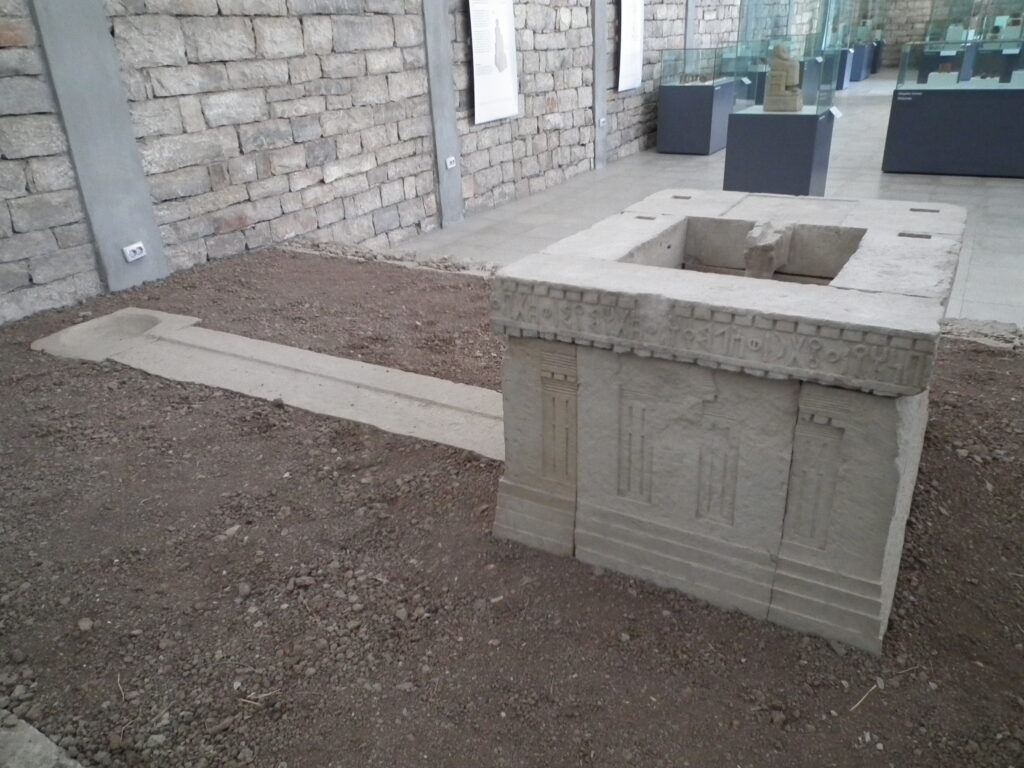

The people who lived in Shabwa were very rich and powerful because they controlled the roads where traders traveled. They made lots of money by selling things like nice-smelling resins called frankincense and myrrh. These smelly things were used in ceremonies, medicine, and making perfumes.

But even though Saba was a strong kingdom, it started to have problems around 2,000 years ago. Other kingdoms became powerful, and the trade routes changed, so Saba wasn’t as important anymore. Eventually, it fell apart because of wars and fighting.
But we still remember the Sabaeans because their stories are in books and stories we hear. The ruins of Shaba remind us of how smart and talented they were. Even today, in Yemen, we can see their influence in the way we live and the things we do. We remember them as one of the first great civilizations in the world.
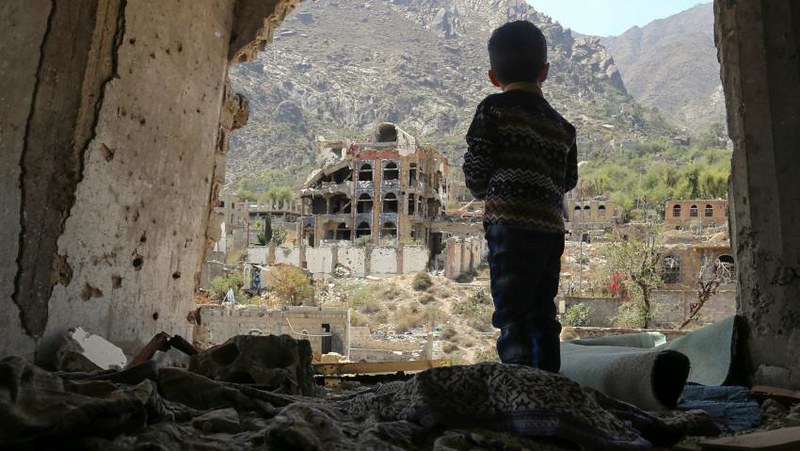

In Yemen today, we can still see traces of the olden days. Places like Sana’a, with its busy markets, and Hadramaut’s rugged mountains, carry reminders of ancient times. The spirit of the Sabaeans, the people of old, lives on in our traditions, the things we do, and the places we live. It shows us how the past can stay alive in the present, teaching us about the long history of our land.

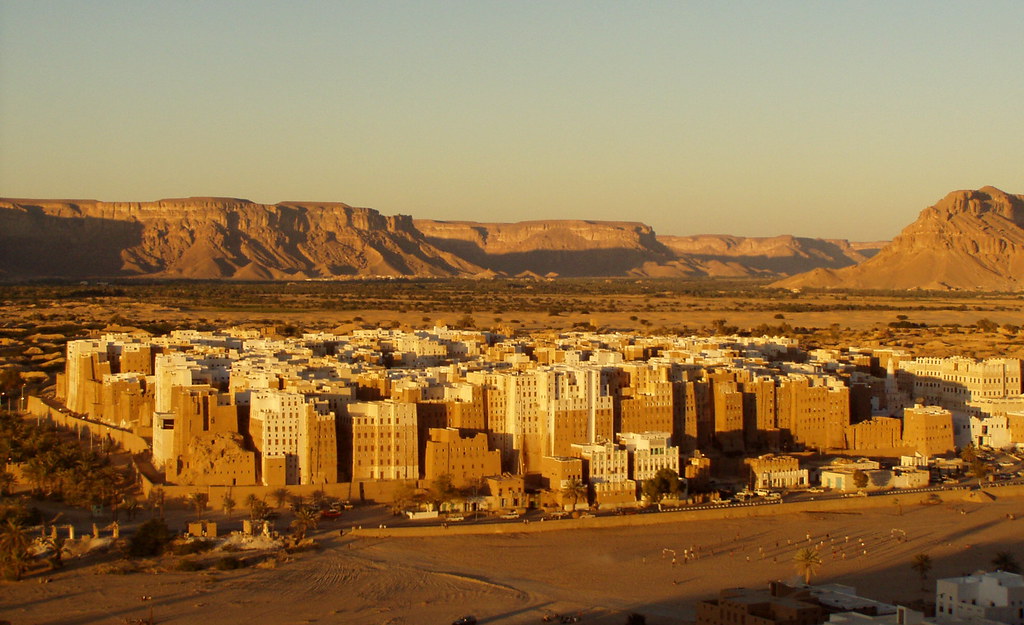
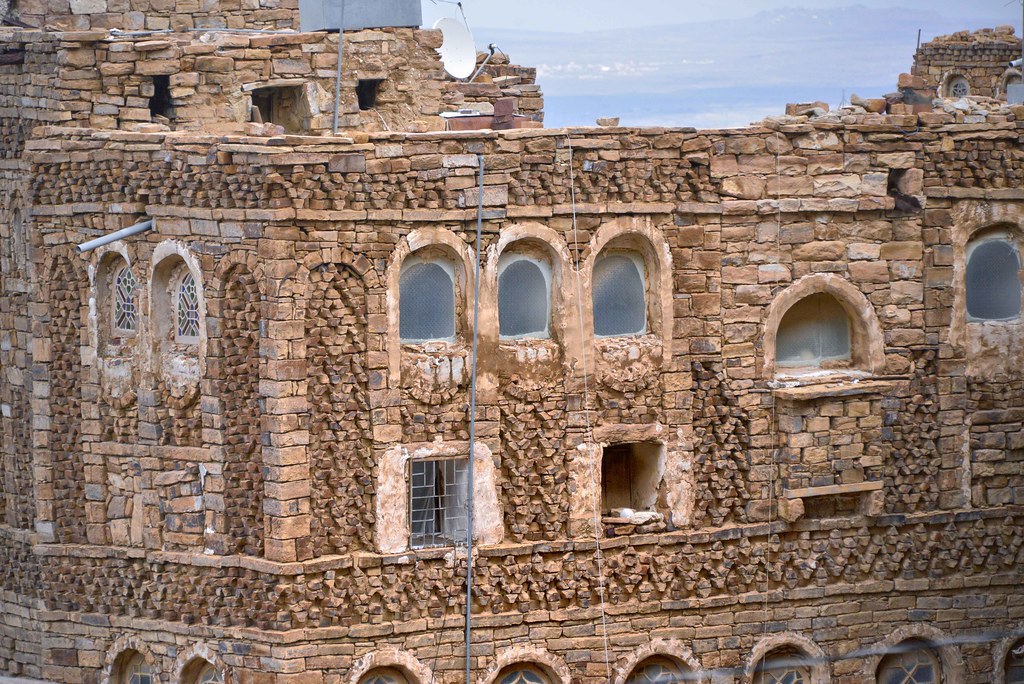
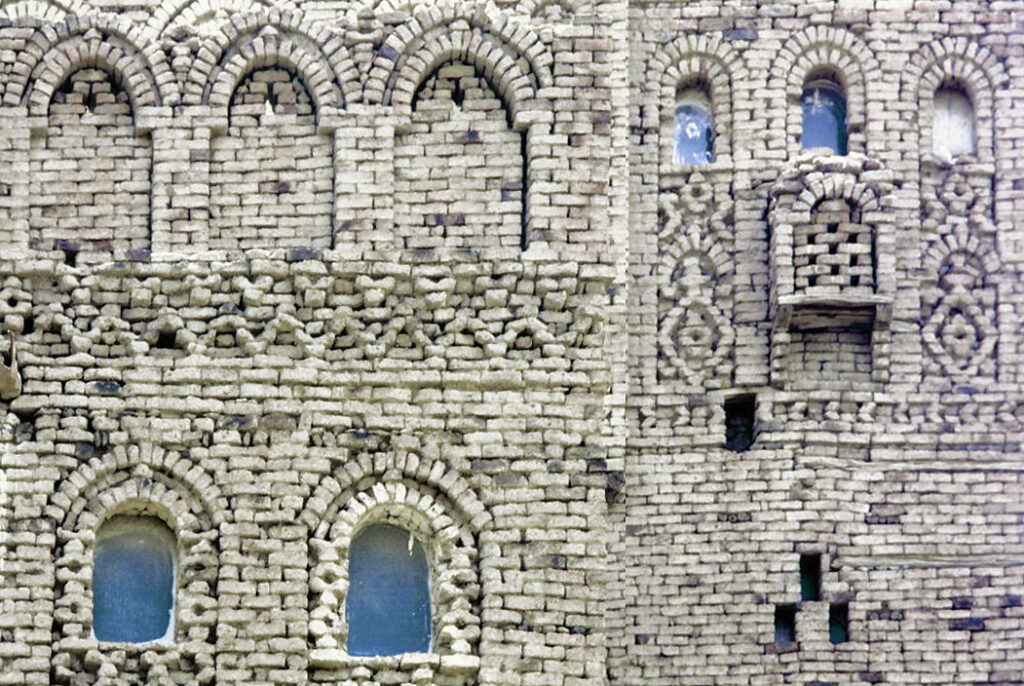
Yemen’s enduring cultural heritage is also evident in its architectural marvels, such as the towering skyscrapers of Shibam. These remarkable mud-brick structures, reaching heights of up to seven stories, have earned Shibam the nickname “the Manhattan of the desert.” Dating back centuries, these skyscrapers were not only marvels of engineering but also symbols of status and prosperity for the city’s residents.

The ancient city of Shibam is not only renowned for its architecture but also for its role as a center of trade and commerce. Situated along key trade routes, Shibam thrived as a hub for the exchange of goods and ideas between the Arabian Peninsula, Africa, and beyond. Its bustling markets bustled with activity as merchants from distant lands converged to trade spices, textiles, and other commodities.

Despite its rich history and cultural significance, Yemen faces numerous challenges in preserving its heritage and promoting tourism. The ongoing conflict and political instability have taken a toll on the country’s infrastructure and economy, making it difficult to attract visitors and investment. However, efforts are underway to safeguard Yemen’s cultural treasures and revitalize its tourism industry, recognizing the potential of heritage tourism to contribute to economic development and national pride.

In conclusion, Yemen’s rich cultural heritage, ancient civilizations, and stunning landscapes make it a treasure trove for historians, archaeologists, and adventurous travelers alike. From the ancient ruins of Saba to the towering skyscrapers of Shibam, Yemen offers a glimpse into the history and culture of one of the oldest civilizations in the world. Despite the challenges it faces, Yemen remains a land of beauty, mystery, and resilience, awaiting discovery by those willing to explore its hidden treasures.

Yemen’s diverse cultural heritage goes far beyond its ancient civilizations and impressive buildings. The traditions and customs found in the country today tell a story of centuries of trade, movement, and sharing between different cultures.
Music is a big part of Yemeni culture, filled with lively rhythms and beautiful melodies that reflect influences from many places, like Arab, African, and South Asian music. Traditional Yemeni instruments such as the oud, qanun, and tabla are often used, giving the music a unique and rich sound.
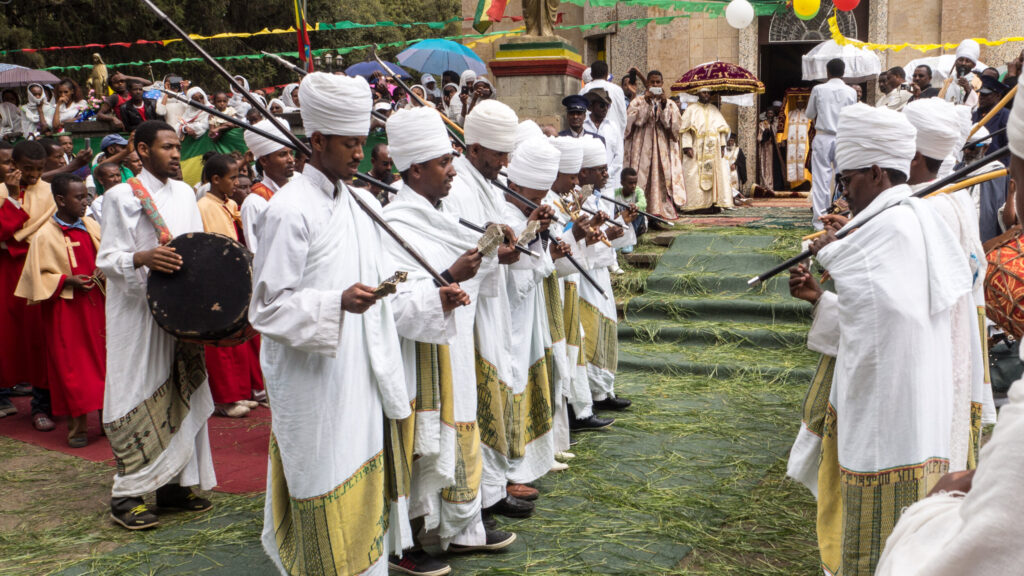

Poetry is also very important in Yemen, with poets being highly respected. Their poems talk about love, nature, and life, and people often gather to listen to them share their verses in gatherings called “mujawarat.”
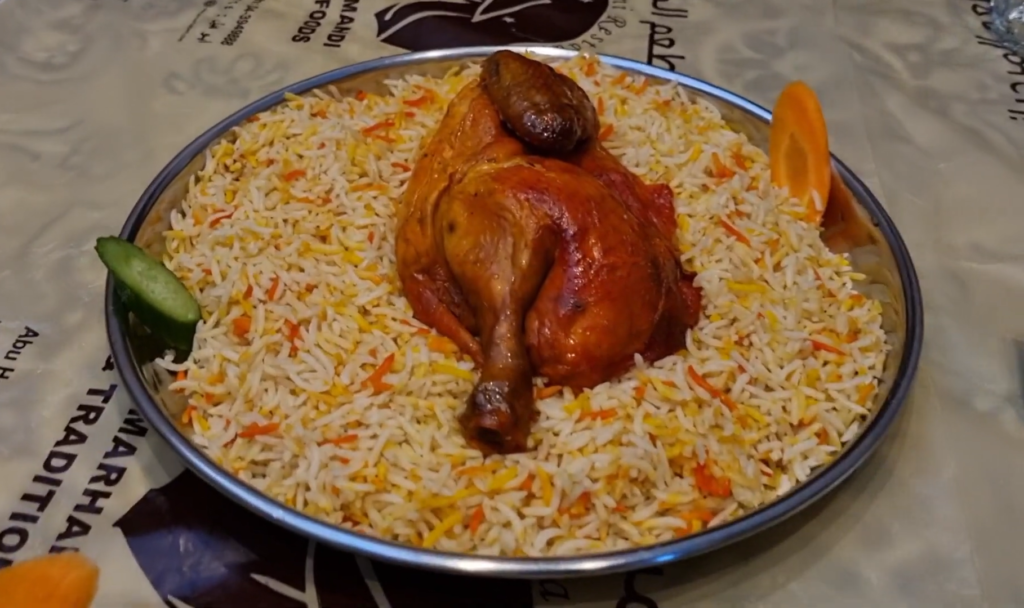
Yemeni food is another highlight, with a wide variety of tasty dishes reflecting the country’s different regions and cultures. Rice, bread, and beans are common staples, and meals are often flavored with spices like cumin, coriander, and cardamom.

Despite facing many challenges like political unrest and environmental problems, Yemen’s people hold onto their cultural traditions with pride. Efforts are being made to protect and promote Yemen’s rich heritage, from preserving historical sites to documenting traditional practices.
As Yemen looks towards a better future, its cultural heritage can be a source of strength and unity. By honoring its past and preserving its cultural identity, Yemen can build a brighter tomorrow for everyone to enjoy and celebrate.
This enduring cultural legacy serves as a beacon of hope amidst the turmoil, reminding Yemenis of their resilience and unity. Despite the hardships they face, Yemenis continue to find comfort and joy in their cultural traditions, whether it’s through music, poetry, or sharing meals with loved ones.

As Yemen strives for peace and stability, preserving its cultural heritage becomes even more vital. By safeguarding their rich traditions and celebrating their diverse cultural identity, Yemenis can forge a path towards a brighter future, filled with pride in their past and hope for generations to come.
Talking more about Yemen’s culture, it’s essential to talk about the many traditions and customs that families in Yemen have followed for a long time.
One of these traditions is celebrating weddings, which are lively and happy times where families and friends come together. Yemeni weddings go on for a few days and are full of colorful ceremonies, fun music, and big meals. People dance traditional dances like the “dabke,” where they join hands and move in a circle to the beat of the music.
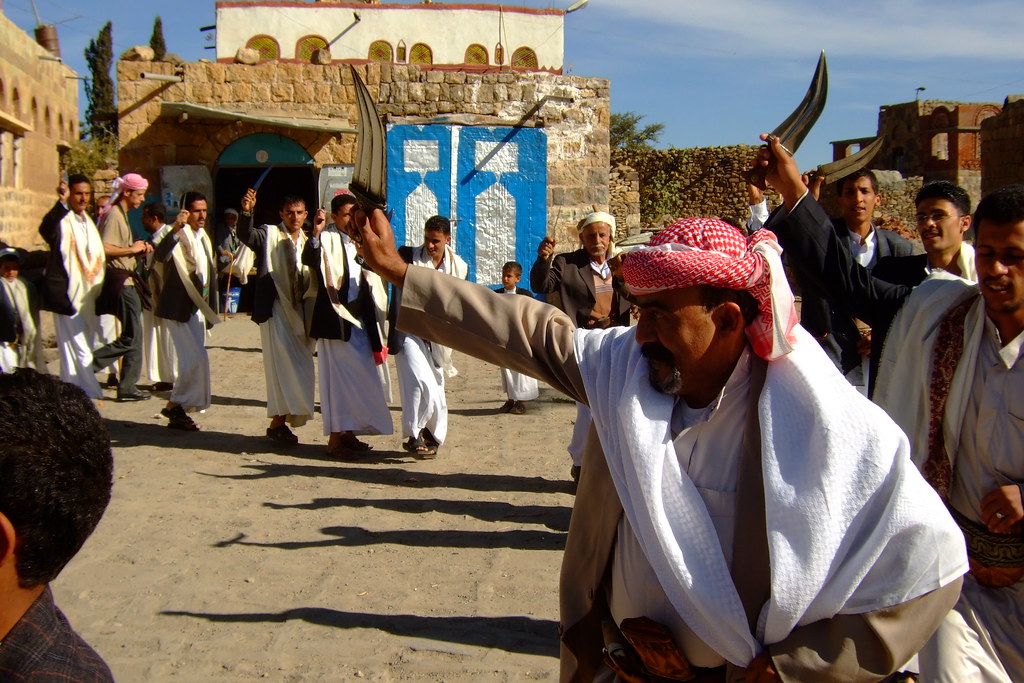

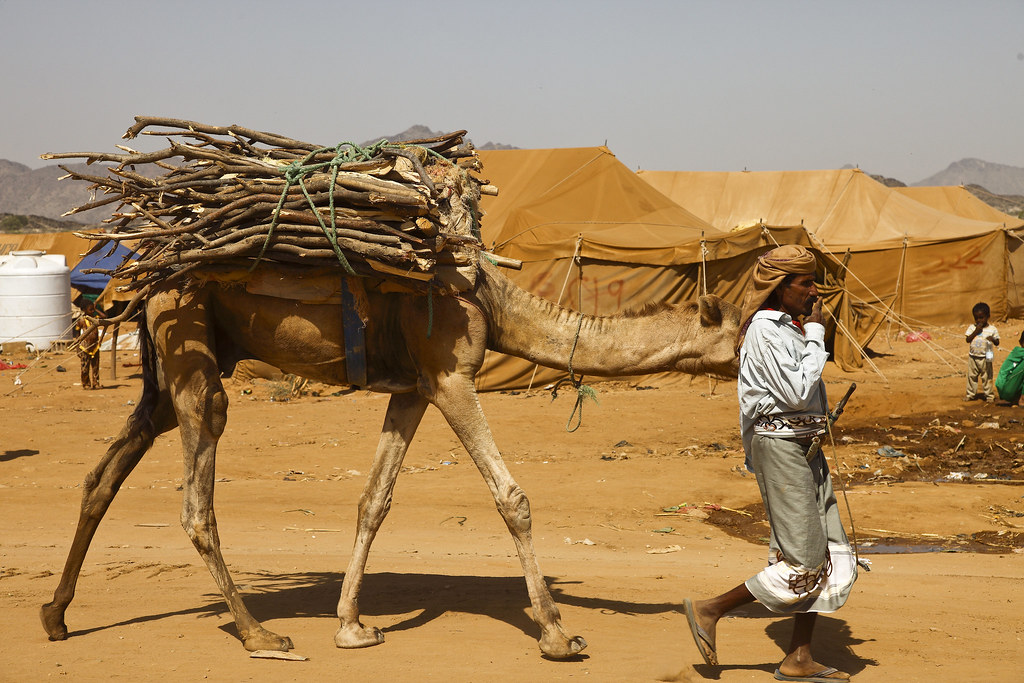
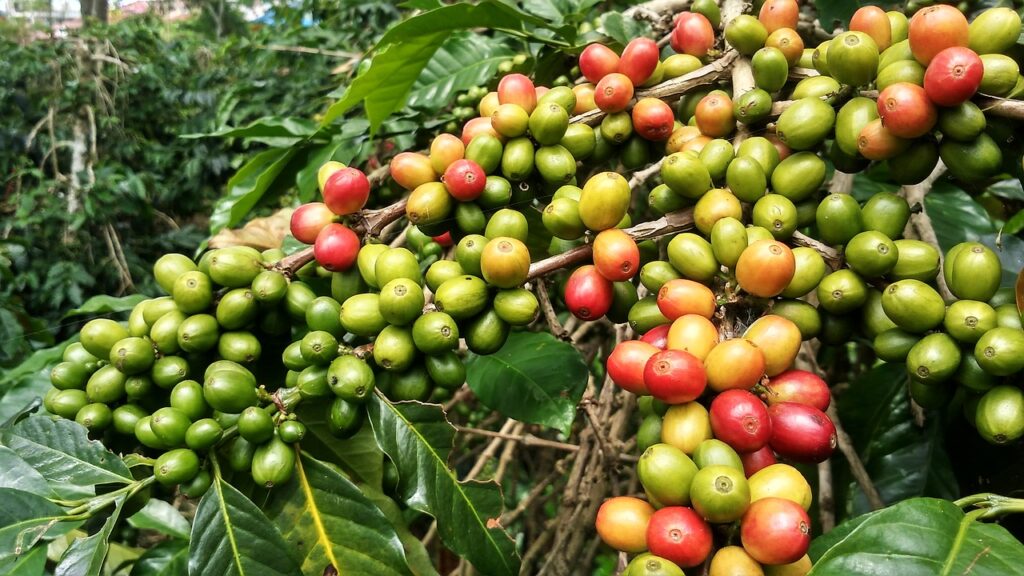
Another important part of Yemeni culture is how connected people are to the land and nature. Farming has always been a big deal in Yemen, with people growing crops like coffee, qat (a plant that gives you energy), and lots of fruits and veggies. The valleys and mountains of Yemen have been home to communities for a long time, providing them with what they need to live.

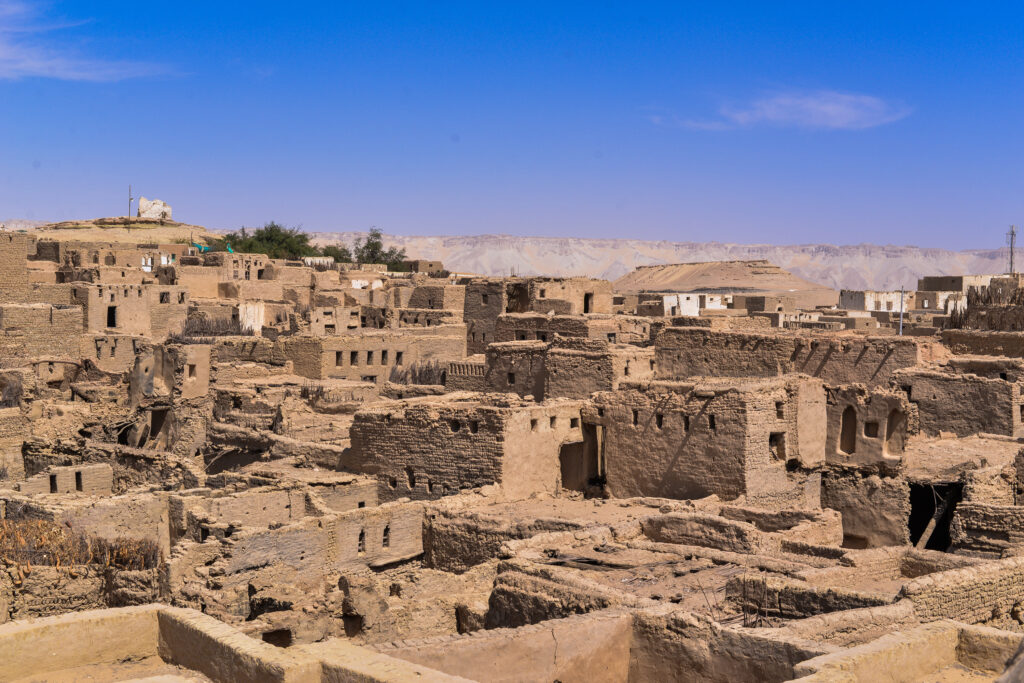
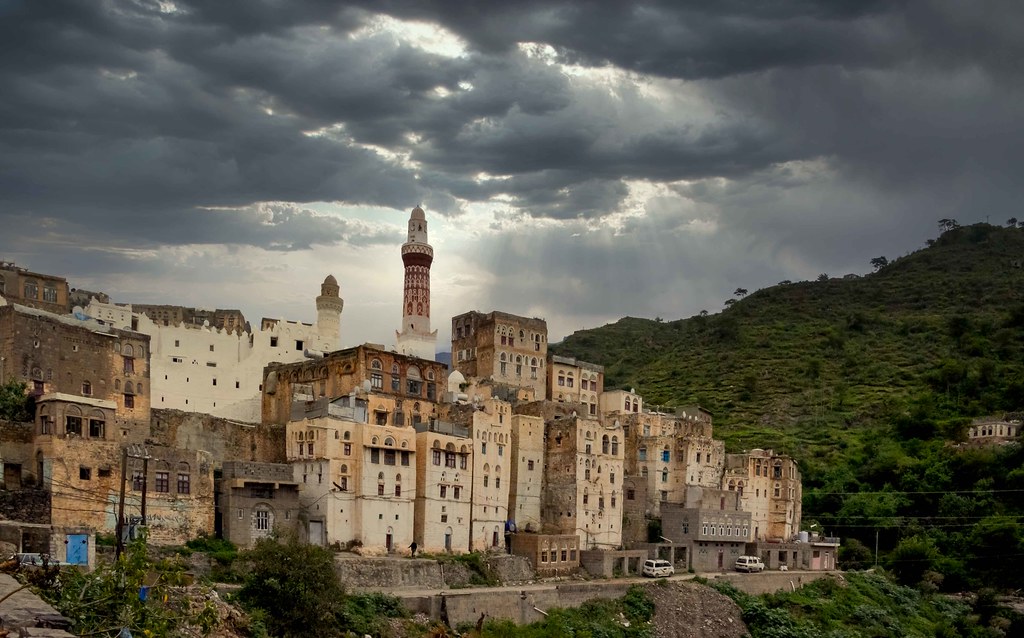
Yemen also has some really cool buildings that show its history and the different influences it’s had. There are tall mud-brick skyscrapers in Shibam, ancient ruins in Marib, and beautiful mosques in Sana’a. Each building tells a story about how creative and skilled Yemeni people are, and how they’ve shared ideas with others over time.

Even though Yemen has some tough problems to deal with right now, like fighting, being poor, and hurting the environment, people still believe in a better tomorrow. Yemenis are known for being strong, friendly, and good at working together. As they work to make things better, their rich culture and history will be a big part of their journey, guiding them and giving them hope for what’s to come.
As Yemen continues to face challenges, its rich cultural heritage remains a source of strength and inspiration for its people. Despite the hardships, Yemenis hold on to their traditions and customs, finding solace and joy in their shared celebrations and deep connection to the land.

Looking towards the future, Yemenis remain hopeful, drawing on their resilience and sense of community to overcome adversity. As efforts to address the country’s pressing needs and foster peace and prosperity continue, Yemen’s vibrant culture will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping its identity and guiding its path forward.
In recent times, more people have become interested in visiting Yemen due to its fascinating cultural history and beautiful natural scenery. Despite facing challenges like political instability and safety worries, Yemen still holds promise for tourism growth.
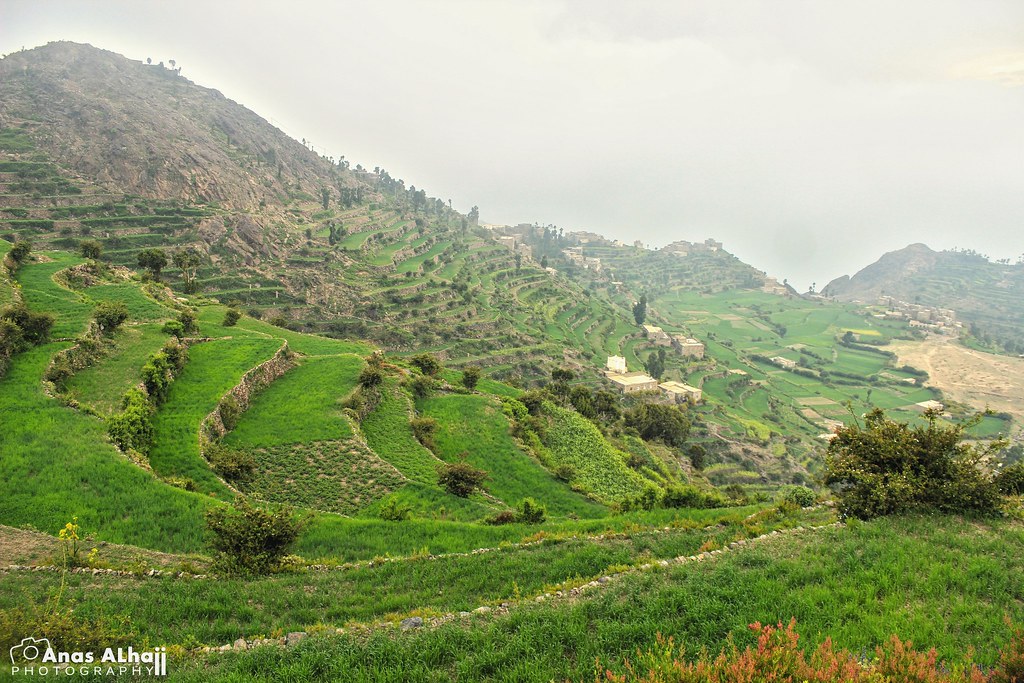

One of Yemen’s main attractions is its breathtaking landscapes, ranging from rugged mountains and green valleys to pristine beaches along the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea. Adventure seekers can explore Socotra Island, known for its unique plants and animals, including the famous Dragon’s Blood trees.
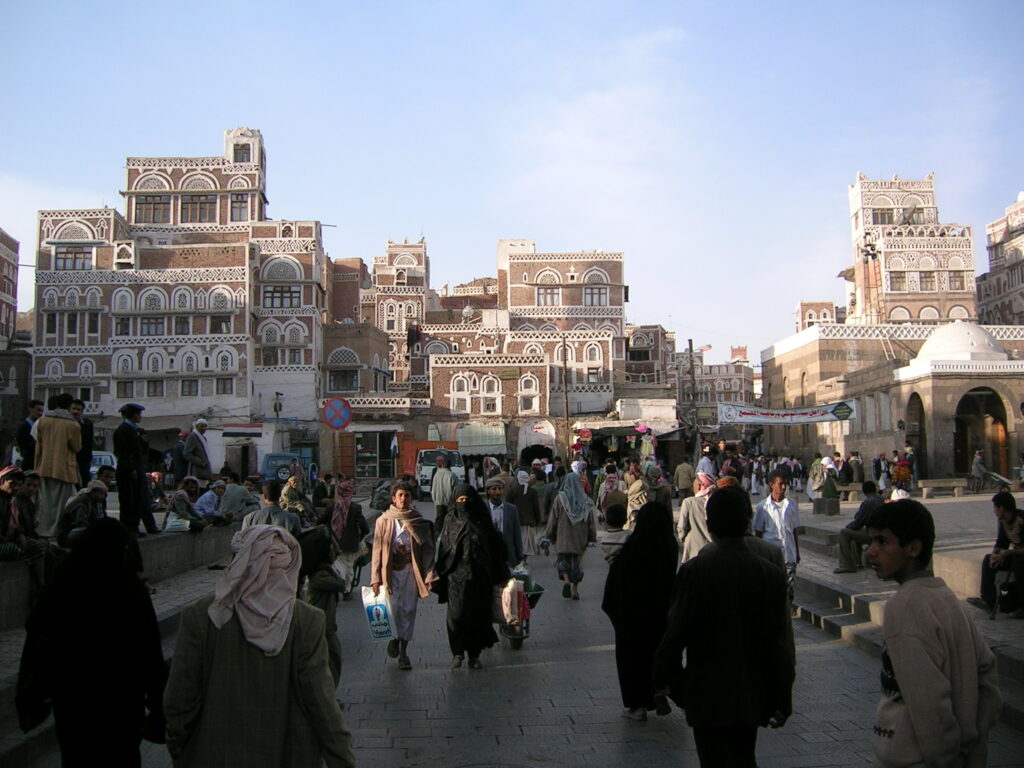
Yemen’s historical sites also offer a glimpse into its past, with ancient cities like Sana’a, Shibam, and Marib showcasing well-preserved buildings and archaeological treasures. Visitors can wander through the narrow streets of Sana’a’s Old City, a UNESCO World Heritage site, admire the tall mud-brick buildings of Shibam, often called the “Manhattan of the desert,” or discover the ancient ruins of Marib, once a thriving hub of the Sabean civilization.
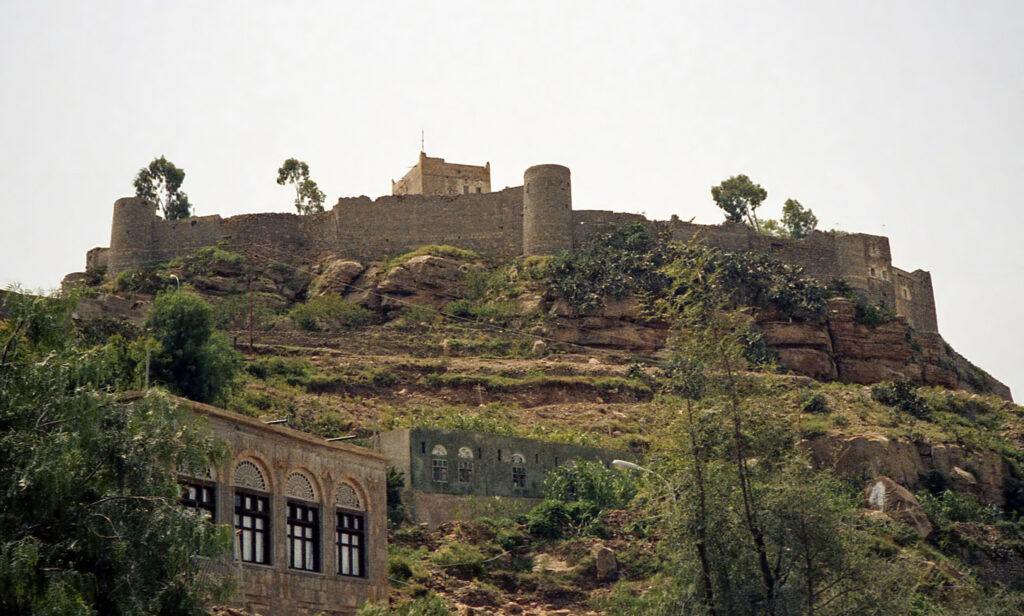

Apart from its cultural and historical appeal, Yemen offers chances for immersive cultural experiences, such as tasting traditional Yemeni food or participating in local events and celebrations. Yemeni cuisine is famous for its rich spices, fragrant herbs, and hearty dishes like mandi (slow-cooked meat and rice) and salta (a flavorful stew).
Although Yemen’s tourism infrastructure is still developing, there’s potential for sustainable tourism initiatives that benefit local communities and protect Yemen’s unique culture and environment. By encouraging responsible travel practices and investing in better infrastructure, Yemen can enjoy the economic advantages of tourism while preserving its distinct identity and natural beauty.
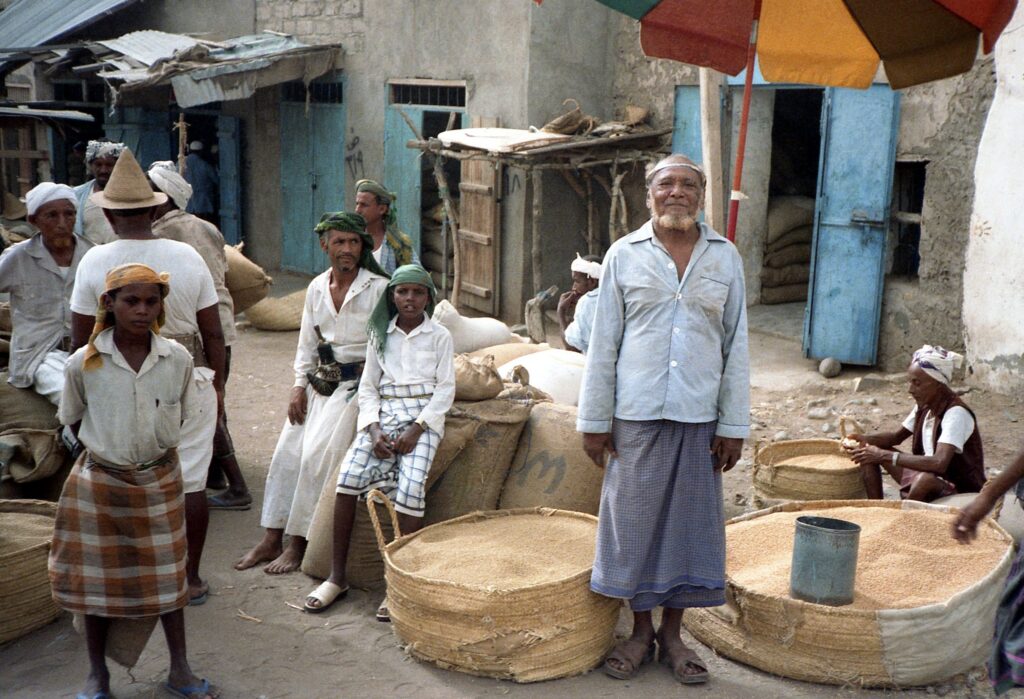

In summary, Yemen’s diverse cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and welcoming atmosphere make it an attractive destination for adventurous travelers seeking authentic experiences. With careful planning and support, Yemen has the opportunity to become a thriving tourism hotspot that honors its past while embracing its future.
Exploring Yemeni Culture and Traditions
Yemen’s cultural heritage is deeply ingrained in its past, customs, and diverse communities. From the lively markets of Sana’a to the tranquil villages in the countryside, Yemen offers a variety of experiences for visitors to discover.
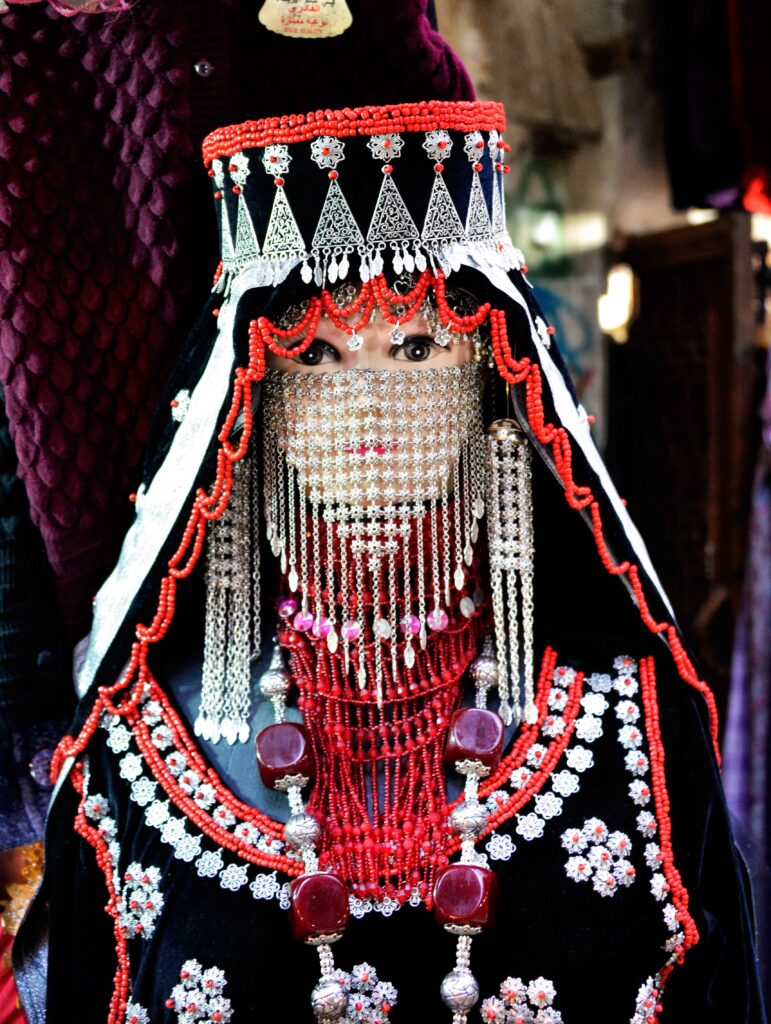

Traditional Yemeni Hospitality:
Yemenis are famous for their warm welcome and generosity towards guests. Visitors are warmly received into homes, where they experience traditional Yemeni hospitality, including aromatic coffee rituals and lavish meals shared with loved ones.
Rich Cultural Traditions:
Yemen’s cultural scene is influenced by a mix of Arab, African, and Islamic cultures. From dynamic music and dance performances to intricate crafts and colorful festivals, Yemeni culture showcases a rich blend of customs and traditions.
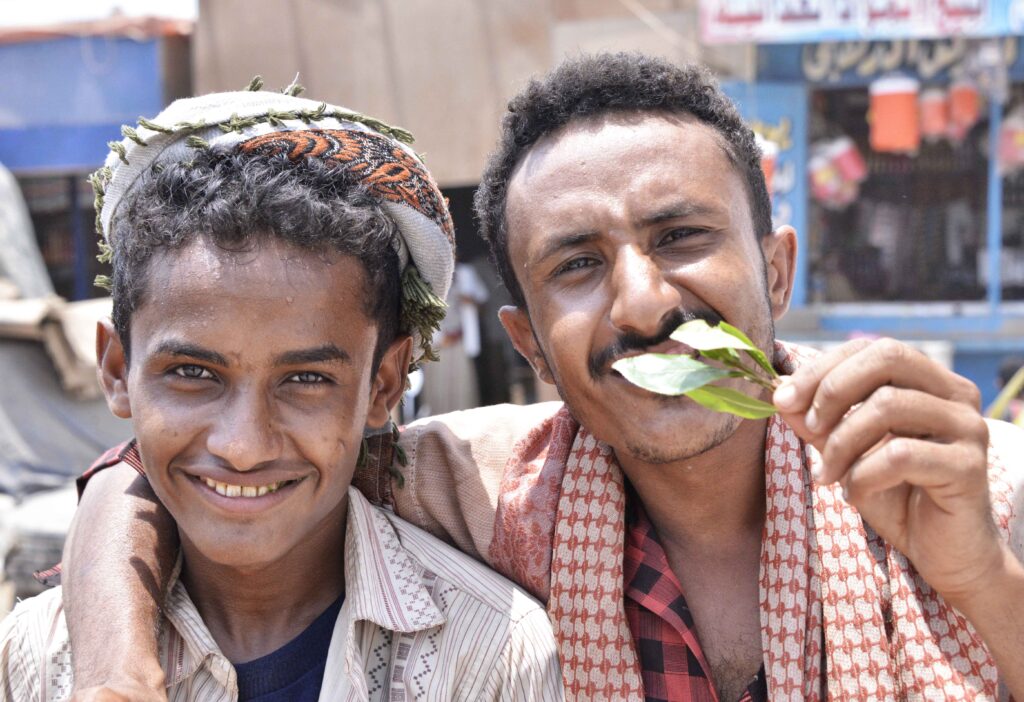

Music and Dance:
Music holds a central place in Yemeni culture, with folk songs and dances expressing emotions like happiness, sadness, and celebration. From the lively beats of the “mahrajan” dance to the soulful melodies of the oud and qanbus instruments, Yemeni music enthralls listeners.
Traditional Dress:
Yemeni clothing reflects the country’s diverse cultural background and regional distinctions. Men often wear the “futa” and “mawaz,” while women dress in vibrant “jilbabs” and elaborate “madhalla” adorned with intricate embroidery and beadwork.

Culinary Delights:
Yemeni cuisine delights the senses with its bold flavors, fragrant spices, and varied culinary traditions. Staple dishes like “mandi,” “salta,” and “fahsa” are enjoyed alongside flatbread and spicy condiments like “zahawiq.”
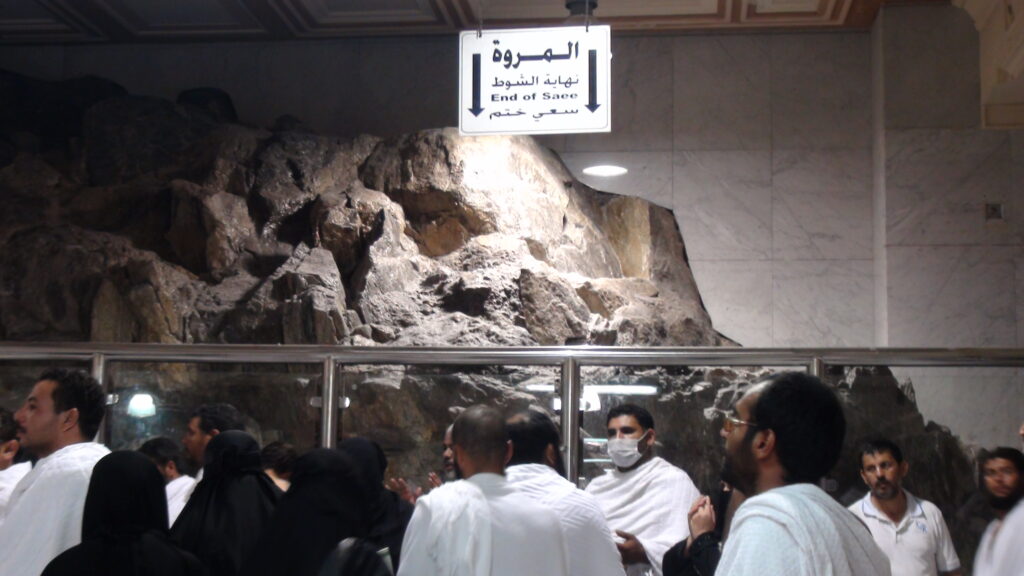
Sacred Sites and Spiritual Practices:
Yemen boasts numerous sacred sites and religious landmarks revered by Muslims worldwide. From ancient mosques in Sana’a to the historic town of Zabid, Yemen’s spiritual legacy is intertwined with its cultural identity, offering visitors a profound sense of connection.

Future Opportunities for Tourism Development
Sustainable Tourism Initiatives:
As Yemen looks to rebuild its tourism industry, there’s an opportunity to focus on sustainable initiatives that promote environmental conservation and community empowerment. Investing in eco-friendly infrastructure and supporting local livelihoods can help preserve Yemen’s natural and cultural heritage.
Cultural Exchange Programs:
Cultural exchange programs provide a chance for travelers to engage with local communities and learn about Yemeni culture firsthand. By facilitating these programs, Yemen can foster greater understanding and appreciation for its rich cultural heritage.

Heritage Tourism Development:
Yemen’s wealth of historical sites presents opportunities for heritage tourism development. By preserving and promoting these cultural assets, Yemen can attract history enthusiasts and curious travelers keen to explore its ancient civilizations.
Community-based Tourism Initiatives:
Community-based tourism empowers local communities to participate in tourism development and preserve traditional lifestyles. Offering authentic cultural experiences and homestays can create economic opportunities and promote cross-cultural exchange.

Digital Tourism Promotion:
In the digital age, leveraging online platforms is crucial for promoting Yemen as a tourism destination. Showcasing its attractions through multimedia content and virtual tours can inspire travelers to explore Yemen’s hidden treasures.
In conclusion, Yemen’s vibrant culture and untapped tourism potential offer opportunities for sustainable development and economic growth. By embracing responsible tourism practices and preserving its cultural heritage, Yemen can unlock its tourism industry’s full potential for future generations.



